Global Configuration Commands
Command Description
config-registerregister Alters the configuration register.
boot system location Specifies location to load IOS.
hostname hostname Changes the name of the Cisco router or switch.
banner motd char banner char Creates a message of the day login banner.
ip host name ipaddress Configures a static mapping of a hostname to an IP address.
ip name-server ip Specifies a DNS server IP address for dynamic name resolution.
ip domain-lookup Enables automatic name resolution.
ip domain-name Assigns a domain name to a Cisco device.
Securing the IOS
First and foremost, ensure that you physically secure access to your Cisco devices so that there are no intentional or unintentional disruptions or access to the device itself.
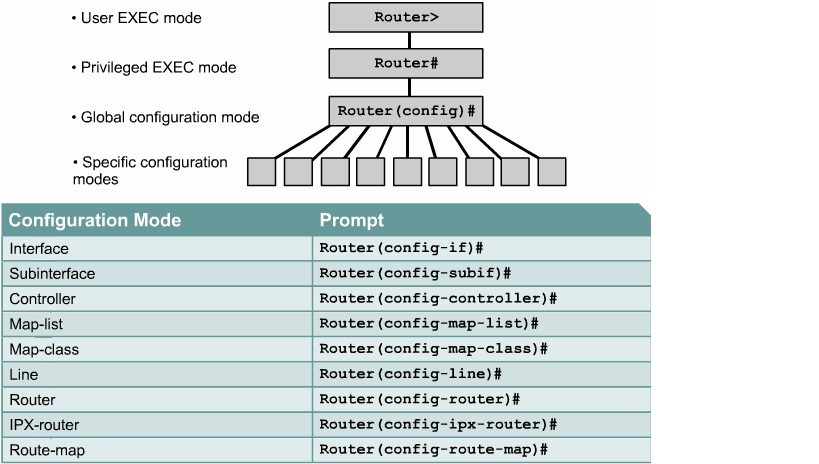
To secure user EXEC access to your console port:
Router(config)#lineconsole 0
Router ( conf ig – line )#login
Router(config-line)#passwordpassword
To secure user EXEC access to your aux port:
Router(config)#lineaux 0 Router ( conf ig – line )#login Router(config-line)#passwordpassword
To secure user EXEC access to all five Telnet lines:
Router(config)#linevty 0 4
Router ( conf ig – line )#login
Router(config-line)#passwordpassword
To secure access to privileged EXEC mode:
Router(config)#enablesecret password Router(config)#enablepassword password
Theenable secret global configuration command encrypts the password using a MD5 hash.If theenable secret andenable password commands are used at the same time, theenable secret password is used.
To encrypt the enable password and the line passwords, use the service password-encryptioncommand.
SSH
To secure terminal access to the Cisco device, use SSH over Telnet. The steps to configure SSH are as follows:
- Configure a hostname on the device other than the default hostname.
- Configure a domain name for the Cisco device.
- Generate an RSA key (recommended to be at least 1024 bits) with the crypto key generate command.
- Create a username/password combination with the username username password password command.
- (Optional) Limit the vty lines to allow SSH with only the transportinput SSH command.
Interface Configuration Commands
Command Description
ip address ipsubnetmask Assigns an IP address to an interface.
no shutdown Administratively enables an interface.
full-duplex
clock rate speed Sets the timing speed of the network on a DCE interface in bps.
bandwidth speed Sets the logical bandwidth setting for routing protocols in Kbps. ip address dhcp
Switch Commands
Switch Configuration Commands
Command Description
interface range media range Configures several interfaces with the same parameters.
ip address ipaddress Assigns an IP address to a VLAN interface.
ip default -gateway ip Sets the gateway of last resort for a Layer 2 switch. Changes the speed of an autosensing link in Mbps. Sets the duplex of a switchport.
The copy Command
Thecopy command is used to copy files from one location to another. For example, to save the current configuration, we copy the running-config in RAM to the startup-config in NVRAM using the copy running-configstartup-configcommand.
Thecopy command is used to copy files between our device and a TFTP server. For instance,copy flashtftpbacks up the IOS in flash to a TFTP server.copy flashtftpcan be usedto upgrade, downgrade, or restore an IOS back onto our device. Before copying to a TFTP server, follow these steps:
- The TFTP server must have the TFTP service running.
- Our device must be cabled correctly. If a switch, plug the TFTP server into the switch with a straight-through Ethernet cable. If going directly between a router and the TFTP server, use a cross-over cable.
- You must have IP connectivity to the server.
- There must be enough room on the TFTP server and your device’s memory to store these files.
The show Command
| General show Commands | |
| Command Mode | Output |
| show running-config Privileged | Current active configuration in RAM. |
| show startup-config Privileged | Configuration stored in NVRAM that is loaded on reboot. |
| show interfaces User and privileged | Status of the interfaces as well as physical and logicaladdress, encapsulation, bandwidth, reliability, load,MTU, duplex, broadcasts, collisions, and frame errors.
Status of the interfaces and their logical addresses. Microcode of the interface including DCE/DTE cable |
| show ipinterfacebriefUser and privilegedshow controller User and privileged | |
| show flash User and privileged | Filenames and sizes of IOS files stored in flash memory. |
| show version User and privileged | IOS version, system uptime, amount of RAM, NVRAM,flash memory, and configuration register. |
Interface Status
| Interface Status Values | ||
| Layer 1 | Layer 2 (Line Protocol) | Possible Symptoms |
| UpUp | UpDown | None. Interface is functional.Encapsulation mismatch, lack of clocking on serial |
| Down | Down | Cable is disconnected or attached to a shutdown inter‑face on the far-end device. |
| Administratively down | Down | Local interface was not enabled with the no shutdown |